Green Steel Making - Innovation & Market
- Boolean IP Team
- Sep 7, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Jul 14, 2024
This report is commissioned to examine the global innovation, market & patenting
trends in the domain of Green Steel Making, in particular based on study of patent
filings after 2000 and secondary market study.
Earliest patent applications in Green Steel Making have been filed in 1990s but a
continuously rising patent activity in this domain started after 2000, with the highest
number of patent applications filed after 2014. Accordingly, this study was restricted
to patents filed after 2000. Looking at high number of filings happening in this domain
by enterprises of all sizes, universities, and researchers etc., it becomes much vital to
have a keen evaluation of the patenting activity to understand the innovation trends.
The initial research aims to give the readers a clear insight regarding the comparative
patenting activity among different players in the domain. A closer look at the patenting
activity demonstrates a constant rise in the filing specifically after 2014 wherein a
steep rise globally can be observed.
This motivated us to take a deeper dive and analyze critically the various techniques
for making green steel. Further, various patent filing trends have been also evaluated
while also revealing the major players in each category. A comparative analysis of R&D
strategy and portfolio strength for few major players have been also evaluated.
Finally, a few driving factors and challenges have been identified in the study. And few
prominent insights and recommendations have been identified that may help the active
players evaluate the scope of their innovation & opportunities of expansion in this
domain.
INTRODUCTION
Steel is the world’s most important engineering and construction material. It is used in
every aspect of our lives; in cars and construction products, refrigerators and washing
machines, cargo ships and surgical scalpels etc. It can be recycled over and over again
without loss of property. Steel has a commendable hardness and strength due to which it is contributing to the technological development in industrial sector.
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon containing less than 2% carbon and 1% manganese
and small amounts of silicon, phosphorus, sulphur, and oxygen. Steel is produced via
two main routes: the blast furnace-basic oxygen furnace (BF-BOF) route and electric
arc furnace (EAF) route. Variations and combinations of production routes also exist.
The key difference between the routes is the type of raw materials they consume. For
the BF-BOF route these are predominantly iron ore, coal, and recycled steel, while the
EAF route produces steel using mainly recycled steel and electricity. Depending on the plant configuration and availability of recycled steel, other sources of metallic iron
such as direct-reduced iron (DRI) or hot metal can also be used in the EAF route.
A total of around 70% of steel is produced using the BF-BOF route. First, iron ores are
reduced to iron, also called hot metal or pig iron. Then the iron is converted to steel in
the BOF. After casting and rolling, the steel is delivered as coil, plate, sections or bars.
Steel made in an EAF uses electricity to melt recycled steel. Additives, such as alloys,
are used to adjust to the desired chemical composition. Electrical energy can be
supplemented with oxygen injected into the EAF. Downstream process stages, such as
casting, reheating and rolling, are similar to those found in the BF-BOF route. About
30% of steel is produced via the EAF route. Another steelmaking technology, the open
hearth furnace (OHF), makes up about 0.4% of global steel production. The OHF
process is very energy-intensive and is in decline owing to its environmental and
economic disadvantages.
Despite being the core pillars of today’s society and providing one of the most
important engineering and construction materials, steel industry now needs to cope with pressure to reduce its carbon footprint from both environmental and economic
perspectives. The amount of CO2 emissions from steel manufacturing is almost double the amount of steel created: 1.85 tonnes of carbon per 1 tonne of steel.
In 2015, the global response to the threat of climate change took a step forward when
190 nations adopted the Paris Agreement. In 2019, the United Nations announced that
over 60 countries—including the United Kingdom and the European Union (with the
exception of Poland)—had committed to carbon neutrality by 2050, although the three
principal emitters China, India, and the United States were not among that number.
Moreover, some nations have pledged to work toward earlier dates. Together, these
agreements have led to growing pressure to pursue decarbonization across all
industrial sectors.
With global steel demand expected to rise to 2.5 billion tonnes per year by 2050, the
environmental burden is growing. Yet an analysis of the overall reduction in worldwide
carbon emissions needed to limit global warming to a maximum of 2 °C above
preindustrial levels—the goal of the 2015 Paris climate agreement—suggests that the
steel industry’s annual emissions must fall to about 500 million tonnes of CO2 by
2050. Achieving that target will require the industry to reduce its carbon intensity
from about 1.85 tonne of CO2 per metric ton of steel to just 0.2 tonne.
This study discusses innovation and market trends since year 2000 and anticipated
future market for green steel.
TECHNIQUES FOR MAKING GREEN STEEL
Steel can be produced via three main processes: using an integrated blast furnace
(BF)/basic oxygen furnace (BOF), an electric arc furnace (EAF), or a direct reduced iron
(DRI)/BOF process. While integrated players produce steel from iron ore and need coal as a reductant, EAF producers use steel scrap or direct reduced iron (DRI) as their main raw material. As the predominant production method globally is the conventional, coal dependent BF/BOF process, the need to assess alternative breakthrough technologies to reduce carbon dioxide emissions is high. The chart below discloses some of the techniques for making green steel.

As BF/BOF efficiency improvement programs only result in an incomplete reduction in
carbon dioxide emissions, they cannot be a long-term solution. Biomass reductants and carbon capture and usage are either only feasible in certain regions or still in the early stages of development. The share of EAFs producing high-quality steel will gradually increase but requires the availability of scrap and DRI. Hence, adopting an approach combining scrap, DRI, and EAF using hydrogen is currently considered the most viable option and the long-term solution to achieving green steel production.
TECHNOLOGY PATENT FILING TRENDS
Below chart shows a trend of patent filing in green steels manufacturing from year
2000-2021. The trend is continuously rising with few dips. It must be noted that
patent filing data is not complete for 2020 and 2021 since most of the patent
applications filed in these years would not have been published till date.

Below chart shows a trend of priority filings in green steel manufacturing from year
2000-2021 in Top 10 Jurisdictions. It must be noted that patent filing data is not
complete for 2020 and 2021 since most of the patent applications filed in these years
would not have been published till date.

OVERALL APPLICATION, GRANT VELOCITY & ESTIMATED EXPIRY
Below chart shows a trend of patent filing in green steel manufacturing from year
2000-2021 and applications’ grant year and expected expiry years. Most number of
applications were granted in this domain in the year 2002. It must be noted that patent
filing data is not complete for 2020 and 2021 since most of the patent applications
filed in these years would not have been published till date.

Non-unique items may be present in this chart. For example; families often contain patents from multiple years, or jurisdictions meaning that in some instances families can be counted more than once (once for each jurisdiction). The assumed expiry date (where applicable) is simply calculated as 20 years from the first grant. Any calculated expiry date further factors in any available specific legal status information. However, both are only as reliable as the data provided by the various jurisdictional patent offices. As with all legal event and status data they in no way constitute legal advice; a qualified patent legal practitioner should always be consulted with regard all pertinent matters.
OVERALL LEGAL EVENTS
Below chart shows the various legal events for all the patent applications in this
domain. A substantial amount of patent applications has been granted.

Below chart shows an active status of patent applications filed in Top 15 jurisdictions.
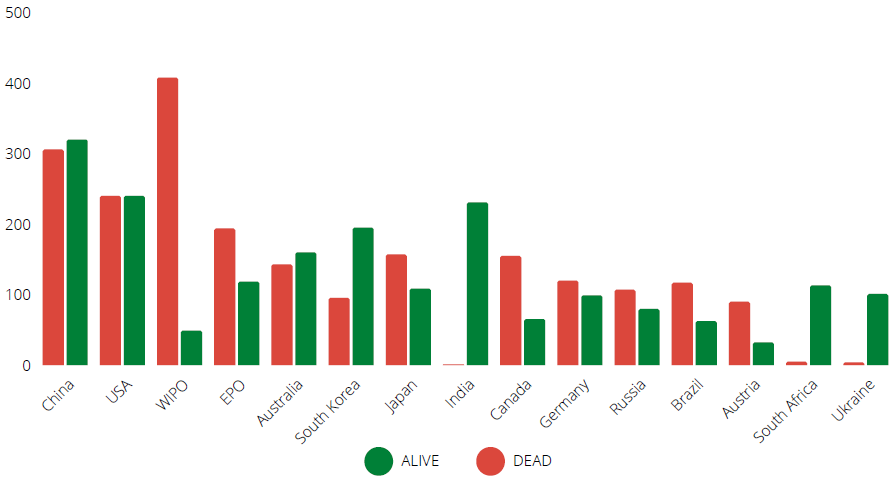
GEOGRAPHICAL COVERAGE OF PATENTING ACTIVITIES
The chart below shows the number of patent families published in Top 10 jurisdictions.
The technology is being protected in these countries which may denote that the
innovators are seeking these geographies as most favorable market for their invention.
More than 30% of the patent applications are filed in China, USA, and Japan.

The chart below shows the number of patent families first filed in Top 10 jurisdictions.
The technology is being first protected in these countries which may denote that the
innovations are originating in these countries. More than 60% of the patent
applications originated in China, Japan, and USA.

ACTIVE PLAYERS AND INNOVATORS
The chart shows the Top 15 players who have filed most applications in this domain.

The chart shows the Top 15 players who have the highest number of granted patents
in this domain.

TOP 5 ASSIGNEES COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
FILING TRENDS



TOP 5 ASSIGNEES COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
TECHNOLOGICAL FOCUS
The chart below shows the technologies for making Green Steel as focused by Top 5
assignees. The patent families for cleanest technology, being 'DRI utilizing green
hydrogen', among identified ones is owned by Posco followed by Primetals
Technology, Kobe Steel, Tata Steel, and Nippon in the respective order.

TOP 5 ASSIGNEES COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
GEOGRAPHICAL COVERAGE



TOP 5 ASSIGNEES COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
LEGAL STATUS


TOP 5 ASSIGNEES COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
PATENT PORTFOLIO STRENGTH
The below chart has been prepared on the basis of relative scores for qualitative and
quantitative parameters to provide a clear comparison for patent portfolio strength for
Top 5 companies working for Green Steel Making. Our cumulative portfolio score
suggests that Kobe Steel has the best patent portfolio among the five assignees.
Though, Kobe's most patents are directed towards improving the efficiency of BF/BOF
and DRI processes.


Get in touch at info@booleanip.com to know more about cumulative portfolio scores.
GLOBAL STEEL MARKET
Over the last 20 years, the global crude steel production has continuously seen a rise
at an average rate of ~4%. The world crude steel production amounted to over 1.95
billion metric tons in 2021, a 3.8% rise compared to 2020. In 2020-21 China has been
the largest producer of crude steel followed by India, Japan, USA and Russia. The
European Union and the United States were the world leading steel importers in 2021,
recording respectively an import volume over 48 and 29 million metric tons. While the
Covid-19 pandemic did not contribute to a noticeable slump in production, a drop in
steel prices negatively impacted revenues from global leaders in the steel market such
as ArcelorMittal and Nucor Corporation.


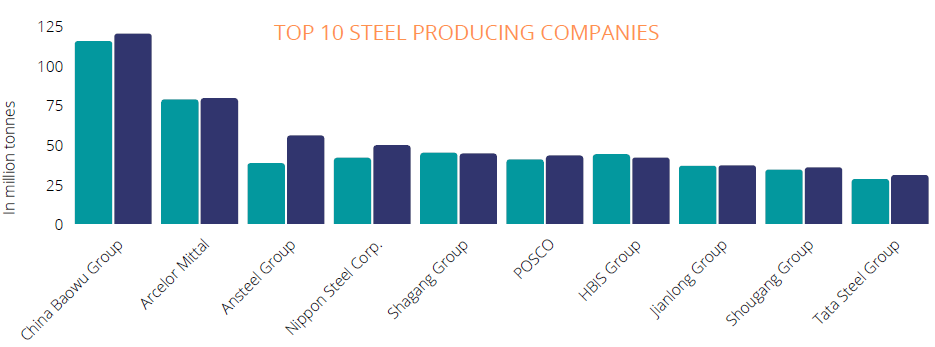
The global steel market is expected to grow at a decent ~4% growth rate in the next
five years. Construction and transportation sector are the major driving factors of steel
market, as they consume two third of the global steel production. In the last two years,
construction and transport steel products has been among the most exported articles.
The global steel demand is expected to grow at 2.2% with the largest consumer being
Asia and Oceania.


GREEN STEEL MARKET - DRIVERS AND CHALLENGES
In 2022, the Global Green Steel Market is in its nascent stage and it is anticipated to
grow at ~5% CAGR till 2027. The stakeholders in the market are progressively
investing in setting up greenfield projects and establishing partnerships & strategic
alliances to transform their businesses. The global market is likely to be driven
primarily by the mounting inclination of governments toward lowering carbon
emissions and adopting sustainable products & manufacturing practices. Manufacturers now recognize that they need to produce steel more environment friendly. Their customers, too, are applying pressure, as they try to hit their own targets linked to indirect emissions.
Although, the technologies for producing green steel already exist such as 'EAF using
DRI' or 'increasing the scrap content in EAFs', there are operational challenges to
these. For running EAFs, power grids globally will need major upgrades to meet the
consumer demands. High quality scrap supply too is limited in quantity, and EAFs
cannot always produce the quality required for certain applications. An EAF using DRI
emits around 1.5 tonnes of CO2, making it dirtier than EAF using scrap but
significantly cleaner than the BF/BOF process. Production could get cleaner still if
hydrogen were to replace natural gas within the DRI process. That way, low-emission
green steel would be possible to manufacture.
According to a report from Bloomberg, steel production could be made with almost no carbon emissions through $278 billion of extra investment by 2050. At present, the
costs to produce green steel are challenging. It is estimated that that a DRI/EAF
process using hydrogen would add about $100 to operating costs per tonne of steel
produced. If, however, the cost of hydrogen were to reduce – to below $1/kg in
Europe and 70 cents/kg in the US – then the technique could be viable. That makes it
imperative for producers to invest in the development of hydrogen-related
infrastructure. Government subsidies and support will be needed to encourage
investment, especially in China, which produced more than 50% of the world’s steel in
2021. Apart from green hydrogen, lack of infrastructure worldwide and labor costs
might pose a challenge for the growth of global green steel market.
RECENT COLLABORATIONS

Hitachi Energy and H2 Green Steel partner to leverage electrification, digitalization, and hydrogen for green steel production. H2 Green Steel will leverage Hitachi Energy’s capabilities to optimize customers’ value chain to plan, build, operate, and maintain the power infrastructure that includes IT and operational technology (OT). The steel production in Boden will use green hydrogen instead of coal in a fully integrated process using end-to end digitalization, which reduces up to 95 percent CO2 emissions compared to traditional steelmaking. This will be equivalent to removing 3 million passenger cars per year from road.

British Petroleum and Thyssenkrupp Steel form strategic collaboration to support decarbonization of steel, including the supply of low carbon hydrogen and renewable power. Thyssenkrupp Steel accounts for 2.5% of CO2 emissions in Germany. By replacing the coal-fired blast furnaces with direct reduction plants where iron ore is reduced with low carbon hydrogen, Thyssenkrupp Steel intends to make steel production climate-neutral in the long term. British Petroleum is focusing on working with corporates in key industrial sectors that have significant carbon emissions to help them decarbonize. The company’s ambition is to be a net zero company by 2050 or sooner, and to help the world to get to net zero.

The Adani group and South Korean steel major POSCO have entered into a deal to explore business cooperation opportunities, including setting up a
green, environment-friendly integrated steel plant at Mundra, Gujarat. The investment is estimated to be up to $5 billion. Both Posco and Adani plan to further collaborate at the group level in other sectors such as renewable energy, hydrogen and logistics to respond to their global carbon reduction requirements. They plan to tap renewable energy sources and green hydrogen, in line with their ESG (environmental, social and governance) commitments to sustainability and energy efficiency.

Rio Tinto has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Germany-based steel production company Salzgitter to work together on carbon-free steelmaking. Under the terms of the MoU, the two companies
will study the optimization of Rio Tinto’s high-quality iron ore products for use in Salzgitter’s SALCOS green steel project in Germany. Rio Tinto produces iron ore pellets and concentrate at its Iron Ore Company of Canada and iron ore lump and fines in Western Australia’s Pilbara region. The collaboration will explore ways to optimize iron ore pellets, lump and fines for use in hydrogen direct reduction steelmaking.

JFE Steel Corporation and Tohoku University jointly announced today that they established the Collaborative Research Laboratory for Green Steel on February 1 to research eco-friendly steel materials and production methods for the carbon-neutral era. The lab will provide an environment for interdisciplinary industrial-academic collaboration between industry engineers and university researchers from February 2022 to March 2025.
Collaborative research at the lab will be targeted at resolving issues to realize low-carbon steelmaking processes through multifaceted approaches. JFE Steel will utilize Tohoku University’s latest numerical analysis technologies in planned experiments.

RWE and Thyssenkrupp plan partnership for green hydrogen based steel production. Green hydrogen from an RWE Generation electrolyzer could help Thyssenkrupp Steel Europe sustainably reduce CO2 emissions from steel production in the future. The energy company and the steel producer have agreed to work together towards a longer-term hydrogen partnership. The first hydrogen is set to flow to the Duisburg steel mill by the middle of the decade.

Vedanta-Iron and Steel Business has recently partnered with IIT Bombay (IIT-B) on an R&D project to develop cost-effective technology for producing Green Steel using hydrogen targeting significant carbon footprint
reduction in Iron and Steel space.
INSIGHTS & CONCLUSION
The study suggests that using DRI (directly reduced iron) by green hydrogen for
making steel in EAF (electric arc furnace) is the cleanest route for making green steel
at present. The primary source of carbon dioxide (CO2) emission in steel making
process is during iron reduction. So, if CO2 emission during iron making is minimized
the overall carbon-neutral steel making is achieved easily. DRI process emits upto 20%
lesser CO2 to as compared to traditional blast furnace (BF) routes. Apart from that,
recycling of scrap iron/steel using EAF is also a good and majorly used technique to
reduce CO2 emission.
Most of the patents filed are related to BF/BOF efficiency improvement programs
followed by DRI route utilizing natural gas to reduce the greenhouse gas emission.
Many recent patents have been filed that disclose using hydrogen for DRI making to
curb the issue of greenhouse emission. Patent activity shows a sudden surge in
innovation and patent filing after 2014, specially in China. More than 60% of the
inventions originated in China, Japan, and USA as suggested by the priority data. Kobe
Steel is leading in terms of number of patent families filed; however most of its
patents are focused on DRI using natural gas and BF/BOF efficiency improvement.
POSCO being second to Kobe Steel holds most number of patents that mention using
hydrogen to reduce ores to solid iron and subsequently using it for steel making. Kobe
Steel and Primetals Technologies respectively own the maximum numbers of granted
patents. More than 50% of the patents filed are alive. Our patent portfolio strength
scores for top 5 assignees (i.e. Kobe Steel, POSCO, Primetals Technologies, Nippon
Steel, and Tata Steel) suggest that POSCO owns better patent portfolio from the
perspective of futuristic technology to achieve greenhouse emission reduction.
The growth market for green steel is in a nascent stage but slowly gaining pace. Many
steel companies have started investing in building the infrastructure to build carbon-neutral steel. Recently in 2021, HYBRIT, a joint initiative of SSAB, LKAB and Vattenfall, have produced the world’s first hydrogen-reduced sponge iron at a pilot scale. The HYBRIT initiative eliminates around 90% of emissions in conjunction with steelmaking. The hydrogen used in the direct reduction process is generated by electrolysis of water with fossil-free electricity, and can be used immediately or stored for later use. Similarly, H2 Green Steel has announced that it has signed customer contracts for more than 5 to 7 years with a range of cross-industry players. The deals cover over 1.5 million tonnes per year out of the planned initial yearly production volume of 2.5 million tonnes, according to the company. Some companies, like Thyssenkrupp aim to feed hydrogen directly into traditional coke-fueled blast furnaces, making use of existing infrastructure to achieve more modest emission reductions. Austria’s Voestalpine is involved in a more radical project called SuSteel that aims to use hydrogen plasma to reduce iron ore.
Despite the promising new steelmaking technologies, they currently operate on a scale that is not ready to completely replace the traditional blast furnaces. Also, although the prices of renewable electricity and green hydrogen are falling fast, the capital costs of setting up new plant, and shuttering old ones, are still a major barrier to change across the industry. This suggests that achieving a net-zero industry requires
perpetual subsidies compared to the current policy and market environment.
There is still a long journey to completely transform the steel industry towards carbon-neutral steel. The shift towards hydrogen-based steel won't happen overnight and is
only one key production technology that can be leveraged to achieve a carbon-neutral
steel industry. Future availability of cheap energy from renewables and regulation will
act as the two key driving aspects for the adoption of hydrogen-based steel. A clear
and clean roadmap must be followed that combines long-term goals with actionable
quick wins to allow for a gradual shift toward green steel that keeps all stakeholders
on board.
Download the pdf report here:
Please feel free to get in touch if you need a similar but more detailed landscape report or valuation report on a technology domain. Also, if you need a patent search partner who not only understands your technology, industry, and needs, but also stay with you on each step during the course of assignment and make sure you get the results crucial for your win, then you are at the right place. Clubbing the experience and expertise of our techno-legal experts, and AI-powered tools, we provide IP Services that help You Succeed. Get in touch with your queries.
#greensteel #fossilfreesteel #carbonneutralsteel #DRI #directlyreducediron #hydrogenDRI #blastfurnace #BOF #EAF #electricarcfurnace #steelmaking #SustainableDevelopmentGoals #SDG #wipogreen #Booleanipconsulting #IPconsulting




Comments